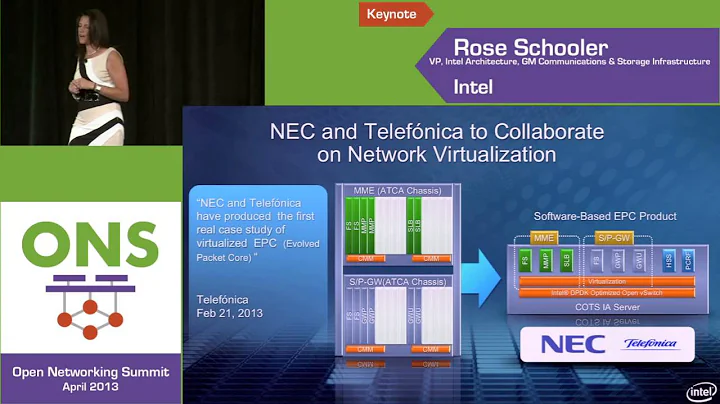
The Ultimate Guide to Applying Thermal Paste
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Thermal Paste?
- The Importance of Thermal Paste
- Different Types of Thermal Paste
- 4.1 Conductive vs Non-conductive Paste
- 4.2 Traditional Thermal Paste
- 4.3 Liquid Metal Thermal Paste
- Methods of Applying Thermal Paste
- 5.1 The Rice Grain Method
- 5.2 The Pea-Sized Dot Method
- 5.3 Spreading Method
- 5.4 X Method
- 5.5 Other Application Techniques
- The Effects of Too Much or Too Little Thermal Paste
- Thermal Paste Performance testing
- Metallic vs Non-Metallic Thermal Paste
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome back everyone! Today, we are going to discuss a topic that we have never covered before on this Channel – thermal paste application methods. Over the years, there has been a lot of debate and various techniques regarding how to apply thermal paste correctly. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of thermal paste, the importance of applying it properly, and the various methods of application. So, let's dive in and demystify the world of thermal paste!
What is Thermal Paste?
Thermal paste, also known as thermal compound or thermal grease, is a substance that is used to facilitate the transfer of heat between two surfaces, usually the CPU and the heatsink. Its primary purpose is to fill the microscopic gaps and imperfections between these surfaces to improve the thermal conductivity and ensure efficient heat dissipation. Thermal paste is essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures and prolonging the lifespan of computer components.
The Importance of Thermal Paste
Proper application of thermal paste is crucial for maintaining the temperature of the CPU within safe limits. When a computer processor operates, it generates a significant amount of heat. Without thermal paste, the heat produced by the CPU cannot be effectively transferred to the heatsink, resulting in poor heat dissipation. This can lead to overheating, performance throttling, and even permanent damage to the CPU. Applying thermal paste correctly helps to ensure that the heat is efficiently conducted away from the processor, thus preventing thermal issues.
Different Types of Thermal Paste
When it comes to thermal paste, there are different types available in the market. Let's take a closer look at some of the common types:
4.1 Conductive vs Non-conductive Paste
Thermal pastes can be broadly categorized into two types: conductive and non-conductive. Conductive thermal paste contains metal particles, such as silver or gold, which enhance its thermal conductivity. It is commonly used in applications where electrical conductivity is desired, such as for CPUs with integrated heat spreaders and GPUs. Non-conductive thermal paste, on the other HAND, does not contain metallic particles and is primarily used in situations where there is a risk of electrical short circuits, such as with exposed electronic components.
4.2 Traditional Thermal Paste
Traditional thermal paste is the most commonly used type and is made from a combination of silicone compounds, metal oxides, and ceramic fillers. It offers good thermal conductivity and is suitable for general-purpose use. Traditional thermal paste is easy to apply and provides reliable heat transfer between the CPU and the heatsink.
4.3 Liquid Metal Thermal Paste
Liquid metal thermal paste, also known as liquid metal compound, is a specialized type of thermal paste that consists of a mixture of metal alloys, such as gallium, indium, and tin. It has extremely high thermal conductivity and is often used by enthusiasts and overclockers to achieve maximum heat dissipation. However, liquid metal thermal paste requires careful application and is not recommended for beginners due to its conductive nature and potentially corrosive properties.
Methods of Applying Thermal Paste
Now that we've covered the basics of thermal paste, let's explore the different methods of applying it. There are several techniques commonly used by enthusiasts and professionals alike. Here are some of the most popular methods:
5.1 The Rice Grain Method
The Rice Grain Method involves placing a small, rice-sized dot of thermal paste in the center of the CPU. When the heatsink is applied, the pressure evenly spreads the thermal paste across the surface. This method is straightforward and ensures the paste covers the necessary areas, although it may sometimes result in slight variations in coverage.
5.2 The Pea-Sized Dot Method
The Pea-Sized Dot Method involves applying a small pea-sized dot of thermal paste onto the center of the CPU. Similar to the Rice Grain Method, the pressure from the heatsink spreads the paste evenly. This method provides consistent coverage, although some enthusiasts argue that it may result in slightly higher temperatures compared to other methods.
5.3 Spreading Method
The Spreading Method involves using a plastic card or spatula to spread a thin, even layer of thermal paste across the entire surface of the CPU. This method ensures complete coverage, but it requires extra care to avoid air bubbles or applying an excessive amount of paste.
5.4 X Method
The X Method involves applying a thin vertical line of thermal paste across the CPU, followed by an equally thin horizontal line intersecting the first line. This creates an "X" Shape. When the heatsink is applied, the pressure spreads the paste evenly in all directions. The X Method is effective in achieving good coverage, but it may require slightly more paste than other methods.
5.5 Other Application Techniques
Apart from the methods Mentioned above, there are various other application techniques, such as the dot with a cross, the line, or the dot with a square. These techniques offer different levels of coverage and consistency, but ultimately their effectiveness depends on proper application and the quality of the thermal paste used.
The Effects of Too Much or Too Little Thermal Paste
Optimal thermal paste application is essential for achieving efficient heat transfer. Applying too much or too little thermal paste can negatively affect thermal performance. If too much paste is applied, it can lead to excess thermal resistance and poor heat dissipation. On the other hand, applying too little paste may result in insufficient coverage and air gaps, leading to increased temperatures and potential overheating. It is important to strike a balance and apply the right amount of thermal paste for optimal results.
Thermal Paste Performance Testing
To assess the performance of different thermal paste application methods, we conducted a series of tests using a variety of methods mentioned earlier. We compared the temperature readings obtained from each method to identify any significant differences. Surprisingly, the results showed minimal variations in temperature among the different application techniques. This suggests that, while the methods may differ in the pattern of thermal paste application, the overall impact on temperature is relatively small.
Metallic vs Non-Metallic Thermal Paste
Another factor to consider when choosing thermal paste is whether to opt for metallic or non-metallic compounds. Metallic thermal paste, such as liquid metal thermal paste, offers higher thermal conductivity due to the presence of metal alloys. This makes it ideal for high-performance systems and extreme overclocking. However, metallic thermal paste requires careful application due to its electrical conductivity and potential for corrosion. Non-metallic thermal paste, like traditional silicone-based pastes, provides good thermal conductivity without the risks associated with metal-based compounds. It is a safer option for most users and offers reliable thermal performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How often should I replace thermal paste?
A: It is generally recommended to replace thermal paste every 1-2 years or whenever you remove the CPU cooler for any reason.
Q: Can I reuse thermal paste?
A: Ideally, it is best to use fresh thermal paste whenever reapplying the CPU cooler. Reusing old thermal paste may result in reduced performance and inefficient heat transfer.
Q: Can thermal paste damage my CPU?
A: When applied properly, thermal paste should not damage the CPU. However, if too much paste is used or it spills onto other components, it can cause electrical shorts or degrade the performance of adjacent components.
Q: What is the best thermal paste for CPU cooling?
A: The best thermal paste for CPU cooling depends on various factors, such as the specific application, performance requirements, and personal preferences. Conductive silicone-based pastes are generally considered to be effective for most users.
Q: Should I clean the old thermal paste before applying new paste?
A: Yes, it is essential to remove the old thermal paste completely before applying new paste. Use isopropyl alcohol and a lint-free cloth or cotton swabs to clean the CPU and heatsink surfaces.
Conclusion
In conclusion, thermal paste is a vital component in ensuring efficient heat transfer between the CPU and the heatsink. Applying thermal paste correctly is crucial for maintaining optimal temperatures and preventing overheating. While there are various application methods and types of thermal paste available, the impact on overall temperature performance is generally minimal. Regardless of the method chosen, it is essential to strike a balance and apply the right amount of thermal paste for optimal results. So, the next time you are upgrading your CPU or reinstalling the heatsink, remember the importance of thermal paste and apply it with confidence!

 134.6K
134.6K
 63.43%
63.43%
 10
10


 7K
7K
 21.72%
21.72%
 3
3

 61K
61K
 31%
31%
 4
4

 5.5K
5.5K
 62.75%
62.75%
 10
10

 < 5K
< 5K
 37.79%
37.79%
 9
9

 < 5K
< 5K
 31.34%
31.34%
 5
5


 < 5K
< 5K
 17.89%
17.89%
 4
4
 WHY YOU SHOULD CHOOSE TOOLIFY
WHY YOU SHOULD CHOOSE TOOLIFY