Unlock Power Efficiency with VIA C3 Socket 370 CPU
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Overview of the VIA C3 Processor
- The Features and Specifications of VIA C3 Processor
- Performance Comparison with Other Processors
- Power Efficiency and Cooling Solutions
- Use Cases and Applications
- Pros and Cons of VIA C3 Processor
- Upgrading Options and Compatibility
- Future of VIA C3 and its Legacy
- Conclusion
Introduction
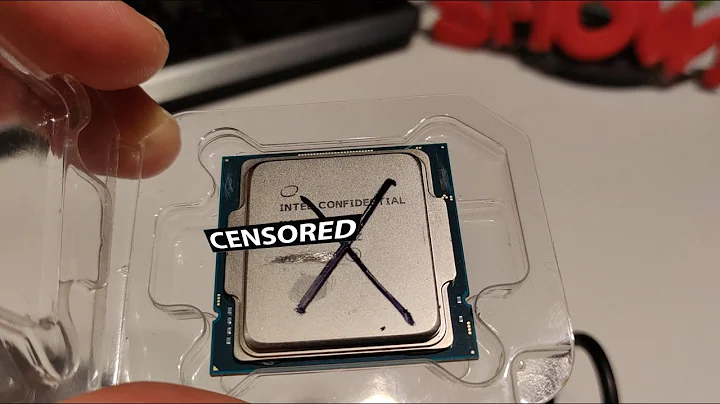
👨💼 Via C3, a processor introduced in January 2003, was known for its power efficiency and low thermal design power (TDP) of only 15 watts. Despite being a 1,000 MHz processor, it gained popularity due to its potential for power-efficient applications and compatibility with Socket 370 Pentium III motherboards. In this article, we will explore the features, performance, and applications of the Via C3 processor, along with its advantages and limitations. Whether you are a tech enthusiast or a curious collector, join us as we delve into the world of this unique processor.
Overview of the VIA C3 Processor
🧐 The Via C3 processor was designed by Centaur Technology and sold by Via Technologies. It was built on the Nehehama core, a significant revision from previous Cyrix processor models. The processor also featured an undocumented alternate instruction set, offering lower-level access and potential privilege escalation. The Via C3 processor was aimed at embedded systems, low-power devices, and budget-oriented applications, making it an attractive option for consumers looking for energy-efficient solutions. In the following sections, we will discuss the features, specifications, and performance of this processor in detail.
The Features and Specifications of VIA C3 Processor
🔍 The Via C3 processor boasted several notable features and specifications, making it a unique offering in the market. With a clock speed of 1,000 MHz and a front-side bus speed of 133 MHz, it provided reasonable performance for its time. The processor had a low TDP of only 15 watts, making it ideal for applications where power efficiency was a priority. It also supported Socket 370, allowing it to be easily installed on existing Pentium III motherboards. However, its small L1 data cache and instruction cache of 16 kilobytes each and an L2 cache of 256 kilobytes limited its overall performance potential. In the next section, we will compare the performance of the Via C3 processor with other processors to assess its capabilities.
Performance Comparison with Other Processors
⚖️ When it comes to performance, the Via C3 processor faced tough competition from processors offered by Intel and AMD. While the Via C3 processor could handle basic tasks and light internet browsing with its 1,000 MHz clock speed, it struggled to match the performance of the more powerful processors in the market. The limited cache size and lower processing power hindered its ability to handle resource-intensive applications and demanding tasks. For users seeking a powerful gaming system or sophisticated multimedia capabilities, the Via C3 processor couldn't deliver the same level of performance as its competitors. However, for specific applications that prioritized power efficiency over raw processing power, the Via C3 processor provided an attractive option. In the following sections, we will explore the power efficiency and cooling solutions of this processor, along with its use cases and applications.
Power Efficiency and Cooling Solutions
💡 One of the major strengths of the Via C3 processor was its exceptional power efficiency. With a TDP of just 15 watts, it consumed significantly less power compared to other processors available during its time. This lower power consumption not only reduced energy costs but also minimized heat generation, making it easier to manage cooling requirements. Given its modest power requirements, the Via C3 processor could be paired with simple cooling solutions, such as air coolers or passive heatsinks. This made it suitable for applications where power consumption and heat management were critical, such as small form factor systems and low-power servers. Despite its power efficiency, the Via C3 processor still faced limitations in terms of raw processing power. Let's explore the specific use cases and applications where it excelled.
Use Cases and Applications
🖥️ The Via C3 processor found its niche in specific use cases and applications that valued power efficiency and low TDP. Its suitability for low-power embedded systems and budget-oriented computing needs made it popular in applications such as thin clients, small business servers, and network appliances. The processor's low power consumption and compatibility with existing Pentium III motherboards also made it a viable option for individuals looking to upgrade their systems within a limited budget. However, due to its limitations in terms of cache size and processing power, the Via C3 processor was not the ideal choice for resource-intensive tasks such as gaming, multimedia editing, or complex computational workloads. In the next section, we will discuss the pros and cons of the Via C3 processor, providing a comprehensive overview of its strengths and weaknesses.
Pros and Cons of VIA C3 Processor
👍 The Via C3 processor offered several advantages that made it an attractive option for certain users. Its low TDP of 15 watts resulted in energy efficiency, reducing overall power consumption and operating costs. The compatibility with Socket 370 Pentium III motherboards allowed for easy upgrades without requiring a motherboard replacement. This made the Via C3 processor a cost-effective solution for users with limited budgets. Additionally, the processor's thermal characteristics allowed for simple cooling solutions, making it suitable for small form factor systems and low-power embedded applications.
👎 However, the Via C3 processor had limitations that buyers had to consider. Its small cache size limited its overall performance potential, making it less capable in resource-intensive tasks compared to more powerful processors in the market. The modest clock speed of 1,000 MHz also hindered its ability to handle demanding applications effectively. These limitations made the Via C3 processor less suitable for tasks such as gaming, multimedia editing, and other processor-intensive workloads. Despite its advantages, buyers needed to carefully evaluate the specific requirements of their intended use cases before considering the Via C3 processor.
Upgrading Options and Compatibility
🔧 Upgrading options and compatibility were crucial considerations for users considering the Via C3 processor. The processor's compatibility with existing Socket 370 Pentium III motherboards allowed for straightforward upgrades without the need for a motherboard replacement. Users could take advantage of the power efficiency and low TDP of the Via C3 processor while preserving their existing systems. However, users needed to ensure that their motherboard supported the 133 MHz front-side bus speed and provided adequate power delivery for the processor. Compatibility issues could arise if the motherboard's BIOS did not support the Via C3 processor or lacked necessary updates. Buyers should carefully consult their motherboard's documentation or manufacturer's guidelines to ensure seamless compatibility.
Future of VIA C3 and its Legacy
🔮 The Via C3 processor has left an indelible mark on the market as a unique offering in terms of power efficiency and low TDP. Although it faced limitations in terms of raw processing power, it found success in specific applications and use cases that valued energy efficiency and low power consumption. While the Via C3 processor may not have maintained its dominance in the rapidly evolving processor market, its legacy lives on in its impact on low-power computing and embedded systems. The advancements in power efficiency and thermal design pioneered by the Via C3 processor continue to influence the development of processors and system designs today.
Conclusion
📝 The Via C3 processor provided a unique solution for users seeking power-efficient computing options with low thermal design power. While it faced limitations in terms of cache size and processing power, its advantages in power efficiency and compatibility with existing systems made it an attractive choice for specific use cases, such as embedded systems and budget-oriented applications. Despite its modest specifications, the Via C3 processor carved its place in the market and contributed to the development of energy-efficient computing solutions. As the processor market continues to evolve, the legacy of the Via C3 processor serves as a testament to the ongoing pursuit of power efficiency and performance optimization in the world of computing.
Highlights
- The VIA C3 processor offered power efficiency with a TDP of only 15 watts.
- It was compatible with Socket 370 Pentium III motherboards, allowing for easy upgrades.
- The small cache size and modest clock speed limited its performance in resource-intensive tasks.
- The processor found use in low-power embedded systems and budget-oriented applications.
- Despite its limitations, the VIA C3 processor paved the way for energy-efficient computing solutions.
FAQ
Q: Can the VIA C3 processor handle gaming and multimedia tasks?
A: While the VIA C3 processor may be capable of basic gaming and multimedia tasks, its limited cache size and modest clock speed make it less suitable for resource-intensive applications in these domains. Users seeking high-performance gaming and multimedia systems would be better served by more powerful processors.
Q: Is the VIA C3 processor compatible with modern motherboard sockets?
A: No, the VIA C3 processor is not compatible with modern motherboard sockets. It is specifically designed for Socket 370 Pentium III motherboards. Users looking to upgrade their systems should ensure compatibility with their motherboard before considering the VIA C3 processor.
Q: Can I use the VIA C3 processor in a small form factor system?
A: Yes, the VIA C3 processor's low thermal design power and power efficiency make it suitable for small form factor systems. It generates less heat and can be paired with simple cooling solutions, making it an attractive option for space-constrained setups.
Q: Are there any upgrading options available for the VIA C3 processor?
A: Upgrading options for the VIA C3 processor are limited as it is designed for Socket 370 Pentium III motherboards. Users can opt for faster variants of the VIA C3 processor if available or consider upgrading to a more modern processor and motherboard combination.
Q: What is the future of the VIA C3 processor?
A: While the VIA C3 processor's market presence has diminished over time, its legacy lives on in the advancement of power-efficient computing solutions. The emphasis on power efficiency and thermal design inspired by the VIA C3 processor continues to influence the development of processors and system designs in the present day.
 WHY YOU SHOULD CHOOSE TOOLIFY
WHY YOU SHOULD CHOOSE TOOLIFY